Print | Kindle(eBook) | Audiobook
Former Procter & Gamble Vice President for IT and Shared Services, Tony Saldanha articulates strategies for leading a successful digital transformation and he also demonstrates how to improve the odds of digital transformation by lowering the costs and risk of change. Saldanha proposes using a five-stage model for digital transformation and a disciplined process for executing it.
The reason why digital transformations fail is that they take more discipline than one might expect. It takes a surprising amount of discipline and a positive outlook of the possibilities for digital transformations to succeed.
The book is about understanding why digital transformations fail as a means to a more important end, which is how to thrive in an industrial revolution. 70 percent of digital transformations fail, to get the 30 percent right requires discipline. The reason why digital transformations fail is that they take more discipline than one might expect. It takes a surprising amount of discipline and a positive outlook of the possibilities for digital transformations to succeed.
Favourite takeaways – Why Digital Transformations Fail
Models: Singapore Digitization, Washington Post, Netflix,
Failed Projects: Obamacare, Denver Airport Baggage System, The McDonald’s “Innovate” Program”
The Industrial Revolutions
First Industrial Revolution: The evolution of society in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries from mostly agrarian to industrial and urban, which was mostly driven by mechanical innovations such as the steam engine.
Second Industrial Revolution: The explosive growth of industries from the late 1800s to the First World War. This was driven by mass-production techniques, electric power, and the internal combustion engine.
Third Industrial Revolution: The widespread change beginning in the 1980s with PCs and the internet, due to new electronic technologies.
Fourth Industrial Revolution: The melding of the physical, digital, and biological worlds today. The major driver is the availability of massive computing capacity at negligible and further plummeting costs. Thus, what used to be physical (e.g., retail stores) can be digital (e.g., online shopping), or what used to be purely biological (e.g., traditional medicine) can be biotech (e.g., personalized genetic medication).
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has digital technology transforming and fusing together the physical, biological, chemical, and information worlds. It’s a force for massive new opportunity in every area valued by society—everything from convenience (e.g., online shopping) and improved health (e.g., biotech) to personal security (e.g., digital homes), food security (e.g., agrotech), and so on.
As with the prior three industrial revolutions, individuals and societies will be affected significantly, and companies will either transform or die.
Disruption vs Transformation
Digital disruption: The effect of the Fourth Industrial Revolution in the corporate and public sector landscapes. Increasingly pervasive and inexpensive digital technology is causing widespread industrial, economic, and social change. This explosive change has occurred only in the past decade or two.
Digital transformation: The migration of enterprises and societies from the Third to the Fourth Industrial Revolution era. For companies, this means having digital technology become the backbone of new products and services, new ways of operation, and new business models.
There are two ways in which digital transformations fail. The lack of discipline causes them to first, fail to take off, and second, to maintain momentum, and they end up crashing.
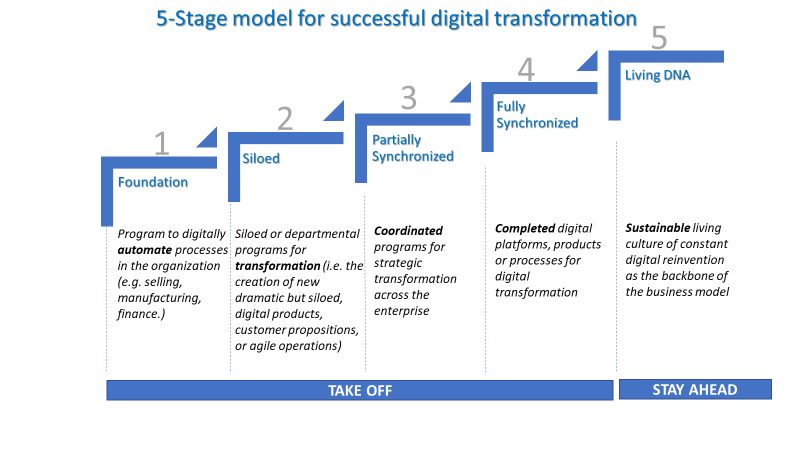
The Five-Stage Digital Transformation Model
The five stage Digital Transformation 5.0 model provides a disciplined road map to succeed in transformation.
Stage 1 is the Foundation. This is where enterprises are actively automating internal processes.
Stage 2 is called Siloed. You might see individual functions or businesses start to use disruptive technologies to create new business models.
Stage 3 is Partially Synchronized transformation. The CEO has recognized the disruptive power of digital technologies and defined a digital future state.
Stage 4, or Fully Synchronized, marks the point where an enterprise-wide digital platform or new business model has fully taken root for the first time.
Stage 5, or Living DNA, is the step where the transformation becomes perpetual.
“An organization can “do” digital as part of a one-time transformation, but to achieve ongoing market leadership it needs to “become” digital.”
Stage 1 is the Foundation. – automation(digitalization)
This is where enterprises are actively automating internal processes, such as selling, manufacturing, or finance, using SAP, Oracle, Salesforce, or similar platforms. This is more automation (also called digitalization) than transformation, but it provides the digitalized foundation necessary for future transformation. Automating processes using digital platforms is necessary to convert manual effort into data.
Automation (or digitalization) of processes. It delivers enterprise value by using technology to do work more efficiently and builds the foundation for further transformation.
Causes of Failure
Teams lose sight of the intended business value being targeted, or they execute poorly.
Disciplines to Address Risks
Committed ownership of the strategy at the highest levels.
“Speed of execution matters in digital transformation not just because digital transformation is an urgent issue but because speed generates enthusiasm, momentum, and the right mindset.“
Stage 2: Siloed
Where you might see individual functions or businesses start to use disruptive technologies to create new business models. So for instance, the manufacturing function may have made progress on using the Internet of Things to drive major changes in the way they manufacture or manage logistics, or the finance manager may have heard about blockchain and transformed the way they do intercompany accounting across countries.
Alternatively, a business unit within the enterprise may have used technology to create a completely new business model, such as selling direct to consumers as opposed to via retailers. The point is that these efforts are siloed, and there is no overall company strategy driving transformation.
Siloed transformations are a microcosm of what will hopefully become higher stages of digital transformation.
Causes of Failure
Common mistakes include under-powering change leaders and making incorrect choices in what to transform.
Disciplines to Address Risks
Disruption empowerment of the change leaders.
Digital leverage points identification.
Partially Synchronized – Partially Synchronized transformation
The enterprise leader, owner, or CEO has recognized the disruptive power of digital technologies and defined a digital future state. At Stage 3, the organization has started rowing in the same direction. However, the enterprise has not completed transforming to a digital backbone or new business models, nor has the agile, innovative culture become sustainable.
Causes of Failure
An ineffective change management strategy or insufficient amount of transformation projects to adequately transform the core organization.
Disciplines to Address Risks
Change management model for effectively transforming the core organization.
Strategy sufficiency in terms of the portfolio of initiatives needed to drive a complete transformation.
“Partial completion of an enterprise-wide strategy for digital transformation. The term “partially” in the title is reflective of part business-outcome delivery, not part synchronization of efforts.”
Stage 4, Fully Synchronized
It marks the point where an enterprise-wide digital platform or new business model has fully taken root. However, it is a one-time transformation. It is still just one technology (or business model) change away from being disrupted. The only way to survive continuous disruption threats is to make digital capabilities and an agile innovative culture an ongoing integral part of the enterprise.
“The point where an enterprise-wide digital platform or new business model has fully taken root. However, it is a one-time transformation. It is still just one technology (or business model) change away from being disrupted”
Causes of Failure
Inability to complete the one-time digital transformation due to either organization structure issues or digital literacy issues.
Disciplines to Address Risks
Digital reorganization to reboot technical capabilities both in the IT function and the rest of the enterprise.
Staying current on the rapidly evolving technology landscape, both for completion of the onetime transformation and its successful ongoing operation.
Stage 5, Living DNA
It is the step where the transformation becomes perpetual. You maintain ongoing industry trend leadership because you are disciplined in constantly innovating and setting industry trends. You’re not just a market leader; you’re a disciplined innovator.
“The stage of perpetual transformation. Constant reinvention and a highly agile culture become second nature to the organization. The enterprise becomes a disciplined market leader.”
Causes of Failure
A loss of the edge that previously delivered a Stage 4 transformation, either due to an insufficiently agile culture or a lack of discipline to constantly sense and respond to new business disruption risks.
Disciplines to Address Risks
Agile culture to support constant evolution of the business and organization.
Sensing risk to the enterprise routinely and reacting to them in a disciplined manner.
Why Are the Warning Signals Ignored?”\
As mentioned earlier, leaders have a sense of their organization’s digital disruption peril already. The bigger question is how much they are reacting to it, and if not enough, then why
The answer to this tends to be sociological—fear, inertia, and misjudgment.
Fear about cannibalizing existing products and about the cost of change. Inertia caused by complacency that the current strategy has historically worked. And finally, misjudgment on the potential impact of digital disruption and an optimistic view of the organization’s ability to withstand the new competition.
All the Best in your quest to get Better. Don’t Settle: Live with Passion.



1 Comment
Pingback: 100 Books Reading Challenge 2021 – Lanre Dahunsi